Appendix B - Defective Conditions of Hose, Tubing and Lines used on Vehicles
All inspection procedures are visual unless additional inspection procedures are indicated or where applied force is necessary to verify tightness and/or component security. The definitions can be found in the “Definitions and Acronyms” section.
Characteristics | Defective Condition | |
|---|---|---|
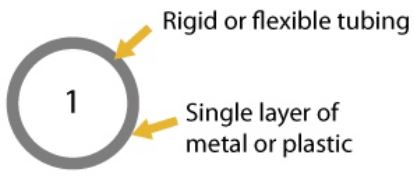
Type 1 – Copper, steel or plastic tubing used for liquid or vapour. Made of a single layer of material. | Damage is visible on the outside that is reducing the wall thickness. | |
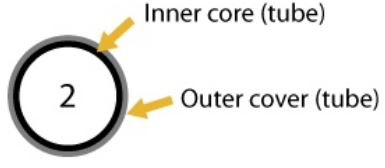
Type 2 – Plastic (usually nylon) tubing commonly used in air brake systems. No reinforcement ply. Inner core and outer cover are usually different colour. | Inner core becomes visible from the outside, as shown by colour change. | |
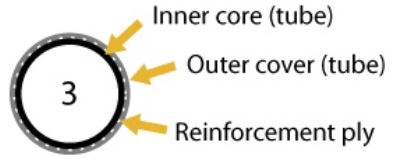
Type 3 – Plastic (usually nylon) tubing commonly used in air brake systems. With reinforcement ply. Inner and outer core are different colour. Note: Type 2 and 3 may appear identical externally. | Reinforcement ply or inner core is visible from the outside, as shown by colour change. | |
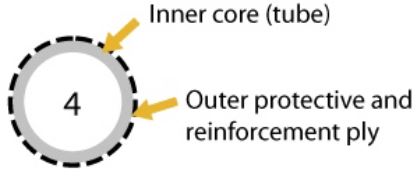
Type 4 – Stainless steel outer cover with inner layer of tubing. | Damage through the outer cover. | |
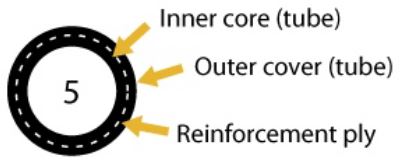
Type 5 – Synthetic rubber hose with inner reinforcement ply. | Wear or damage exposing the reinforcement ply. | |
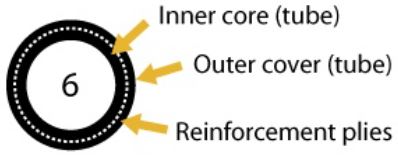
Type 6 – Synthetic rubber hose with multiple reinforcement plies. | Wear or damage exposing the outer reinforcement ply. | |
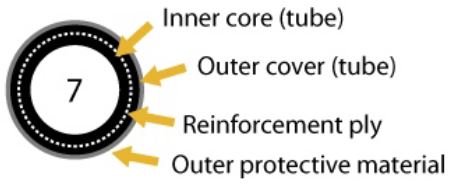
Type 7 – Flexible hose with one or more reinforcement plies that may be fabric or steel, and an outer protective layer. | Wear or damage through the outer protective layer and outer cover, exposing a reinforcement ply. |